In recent years, 3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing processes across various industries. Among the myriad of materials used in this cutting-edge technology, polymers stand out for their versatility, affordability, and ease of use. From prototypes to end-use products, polymer 3D printing has emerged as a game-changer.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of 3D printing with polymers, exploring its applications, technologies, and future prospects. Moreover, we will also look at how to buy polymers online seamlessly, ensuring a secure and safe procurement experience.
The Insight into 3D Printing With Polymers
Polymer 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves layer-by-layer deposition of polymer materials to create three-dimensional objects. This process offers numerous advantages, including rapid prototyping, customization, and cost-effectiveness. Polymers, long-chain molecules composed of repeating subunits, serve as the building blocks in this additive manufacturing process.
Various techniques, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), are used to deposit and solidify the polymer material according to the specific requirements of the printing process.
Moreover, if you want to buy or sell polymers online in order to try 3D printing with them, download the PolyMart Buyer App and make an informed business decision.
The Most Useful Polymer Materials for 3D Printing Purposes
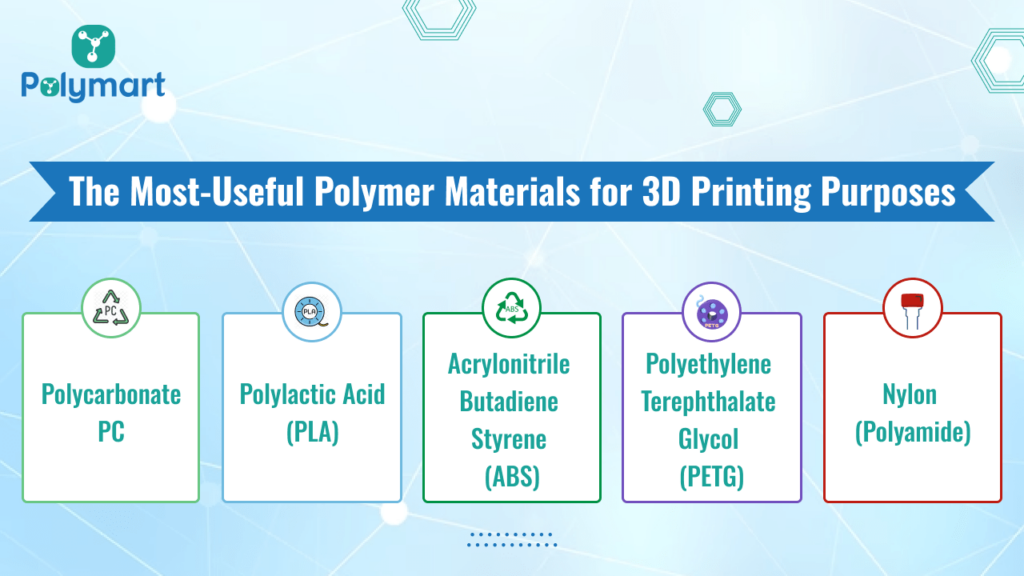
When it comes to 3D printing, the choice of polymer materials plays a crucial role in determining the properties and characteristics of the printed objects. Various types of polymers are utilized in 3D printing, each offering unique features suited to different applications. Here are some commonly used polymers for 3D printing:
Polycarbonate (PC):
PC is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength, impact resistance, and optical clarity. In 3D printing, PC is favored for producing parts requiring high toughness and heat resistance, such as automotive components, electronic enclosures, and medical devices.
Polylactic Acid (PLA):
PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is widely used in filament-based 3D printing due to its low cost, ease of printing, and environmental sustainability.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS):
ABS is a popular thermoplastic known for its durability and impact resistance. It is commonly used in industrial-grade 3D printers for producing functional prototypes and end-use parts.
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG):
PETG combines the strength and durability of ABS with the ease of printing of PLA. It is suitable for applications requiring chemical resistance and transparency, making it ideal for medical devices and food containers.
Nylon (Polyamide):
Nylon is a versatile thermoplastic known for its high strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance. It is commonly used in selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing for producing functional prototypes and end-use parts.
The Most Common Applications of 3D Printing Polymers
As the technology continues to advance and become more accessible, the following are the most common applications of 3D printing polymers:
Prototyping:
One of the primary applications of 3D printing polymers is in rapid prototyping. Engineers and designers use this technology to create physical prototypes of their designs quickly and cost-effectively.
Customized Products:
3D printing polymers enable the creation of highly customized products tailored to individual needs and specifications. In industries like healthcare, personalized medical implants, prosthetics, and orthotics can be produced to match patients’ unique anatomical requirements.
Tooling and Jigs:
3D printing polymers to produce custom tooling, fixtures, and jigs used in various manufacturing processes. These customized tools can improve production efficiency, enhance accuracy, and reduce costs by eliminating the need for traditional machining methods.
Functional Parts:
From automotive components and aerospace parts to consumer electronics and household appliances, 3D printing allows for the production of lightweight, durable, and complex parts with excellent mechanical properties.
Educational and Research Purposes:
Students and researchers can gain hands-on experience with additive manufacturing technology, explore design concepts, and develop innovative solutions across various disciplines.
Final Thoughts: Buy Polymers Online for 3D Printing!
Polymers, being the backbone of 3D printing, offer a plethora of advantages. This technology can effectively utilize an array of commercially available polymers, including acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polylactic acid (PLA), polycarbonate (PC), and so forth. Each of these polymers possesses unique properties, making them suitable for diverse applications.
PolyMart– a leading polymer distribution company, has vast experience in meeting the diverse polymer needs of businesses. To ensure an efficient and hassle-free polymer procurement process, we have designed a PolyMart app for buyers and sellers, who struggle to make well-informed decisions in the dynamic market landscape. Install an app on your device and connect with genuine polymer buyers and sellers near you.