
Polycarbonate is a fascinating polymer known for its exceptional strength, durability, and transparency. From safety helmets to eyeglass lenses, from electronic device housings to food storage containers, Polycarbonate is utilised in numerous industries and products due to its unique combination of properties.
But what exactly is polycarbonate polymer? According to studies, there are over 200 polymer grades available in the market, each varied in their specific properties and polymerization processes. Here, we’re focusing on one of the most common polymers encountered in our daily lives. So, without further ado, let’s delve into and understand the meaning and importance of polycarbonate (PC) polymers.
What is Polycarbonate PC Polymer?
Polycarbonate, often abbreviated as PC, is a type of thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional durability, strength, and transparency. It belongs to the group of polyesters and is derived from bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene. Polycarbonate is widely used in various industries because of its unique combination of properties.
In the manufacturing process, BPA and phosgene are reacted together under controlled conditions, typically in the presence of a catalyst, to form polycarbonate chains. These chains then undergo further processing, such as extrusion or injection molding, to shape them into the desired products.
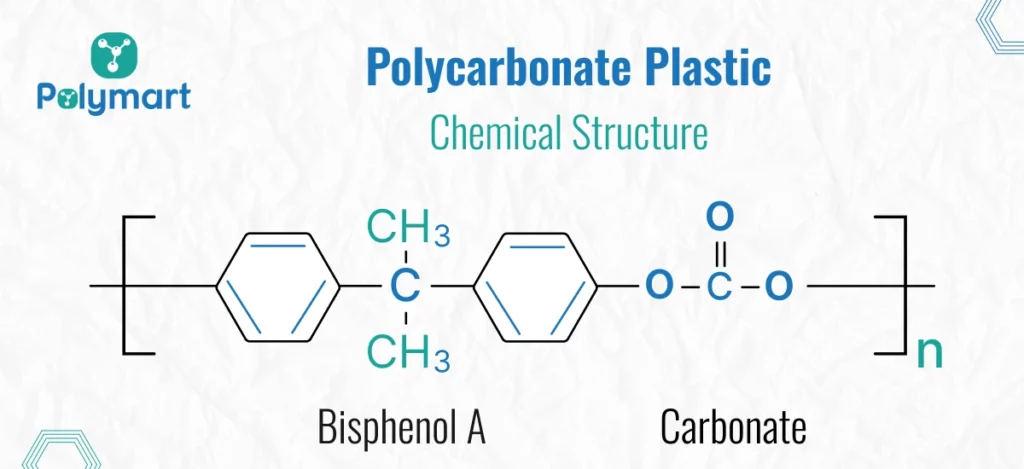
The unique molecular structure of polycarbonate contributes to its outstanding mechanical properties, including high impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for applications where safety and reliability are paramount.
What are the Key Properties of Polycarbonate PC Polymers?
The following key properties make Polycarbonate polymers highly versatile and suitable for various applications across industries.
Polycarbonate Properties
Transparency: 89%
Elongation to fracture: 110%
Glass transition temperature: 150 °C
Shear strength: 9,200 psi
Flexural strength: 13,000 psi
Tensile strength: 70 N/mm²
Young’s modulus: 2.4 GPa
Note: Polycarbonate properties depend on its molecular mass and structure, so each material is slightly different.
What are the Strengths & Limitations of Polycarbonate PC Polymers?
Polycarbonate polymers are ubiquitous in various applications due to their exceptional strength and versatility. However, like any other polymer material, they also have their limitations. Understanding their strengths and limitations is crucial in making informed decisions for your applications. The following are some to note down.
Strengths of Polycarbonate Polymers
• High impact resistance
• Crystal-clear transparency
• Impressive temperature resistance
• Formidable chemical endurance
• Easy processing method
• UV resistance
Limitations of Polycarbonate Polymers
• Scratch sensitivity
• Flammability
• Chemical sensitivity
• Quite costly
• Environmental concerns
• Not suitable for food contact
Are Polycarbonate Polymers Safe to Use?
The safety of polycarbonate polymers is a topic of concern for many, particularly in applications involving human health and safety. Polycarbonate polymers have undergone rigorous testing and have been deemed safe for a wide range of applications. It is generally safe, but some non-food-grade polycarbonates can release bisphenol A (BPA) when they come into contact with water and food.
It is important to remember that FDA compliance standards are set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which ensures that all materials used for food contact are safe, non-toxic, and free of harmful chemicals. The FDA does not approve polycarbonate, but certain grades of these plastic polymers do.
In a nutshell, it’s safe to use polycarbonate for food contact applications. However, some studies have shown that BPA poses a hazardous health risk. This led us to choose “BPA-free” polycarbonate products.
What are the Uses of Polycarbonate PC Polymers?
Polycarbonate PC polymers are highly suitable for applications that demand robust strength and greater durability. The example below highlights PC polymers’ versatility and utility across a wide range of industrial applications.
Safety Equipment: Helmets, face shields, and protective eyewear.
Consumer Electronics: Device housings, display screens, and optical discs.
Automotive Parts: Headlights, interior trim, and dashboard components.
Construction Materials: Skylights, roofing materials, and safety glazing.
Optical Applications: Eyeglass lenses, safety goggles, and camera lenses.
How to Buy Polycarbonate PC Polymers Online?
If looking forward to buying polycarbonate polymers online, your search ends with us. PolyMart – a leading polymer distribution company in India, provides a platform where buyers and sellers can meet their polymer needs under one roof, making it extremely convenient for buyers and sellers to place orders online.
Installing PolyMart made polymer procurement not only simpler, but it kept you aware of daily polymer price trends, allowing you to make informed choices. Download the app on your device and get in touch with our team if you have any further questions!
Polymers in Electronics: Why Are They on the Rise?
[…] like metals, polymers are significantly lighter while maintaining strength and durability. Polycarbonate (PC), for example, is ideal for optical discs, electronic housings, and connectors, offering resilience […]
Comments are closed.